3D Printing Technology
3D Printing Technology
3D Printing Technology
3D printing has become one of the most revolutionary technologies in recent years. It has changed the way products are designed and manufactured, creating new opportunities for businesses and individuals alike. From medical devices to aerospace components, 3D printing technologies have a wide range of applications that are being explored in a variety of industries. In this blog post, we will take a look at 3D printing technologies and how they can be used to unlock the future.
Introduction to 3D Printing Technology
3D printing is a revolutionary form of manufacturing technology that creates three-dimensional objects from digital blueprints. It works by laying down successive layers of material until the desired shape is achieved. 3D printing is used in a variety of industries, from aerospace to medical, and is being used to create products more quickly and cost-effectively than ever before. 3D printing technologies have been around since the 1980s, but they have only recently gained traction due to advances in the materials and software used to create 3D models. There are many different 3D printing materials available, from plastics to metals and even ceramics. There are also a variety of 3D printing software options, ranging from open-source programs to professional-grade modeling suites.
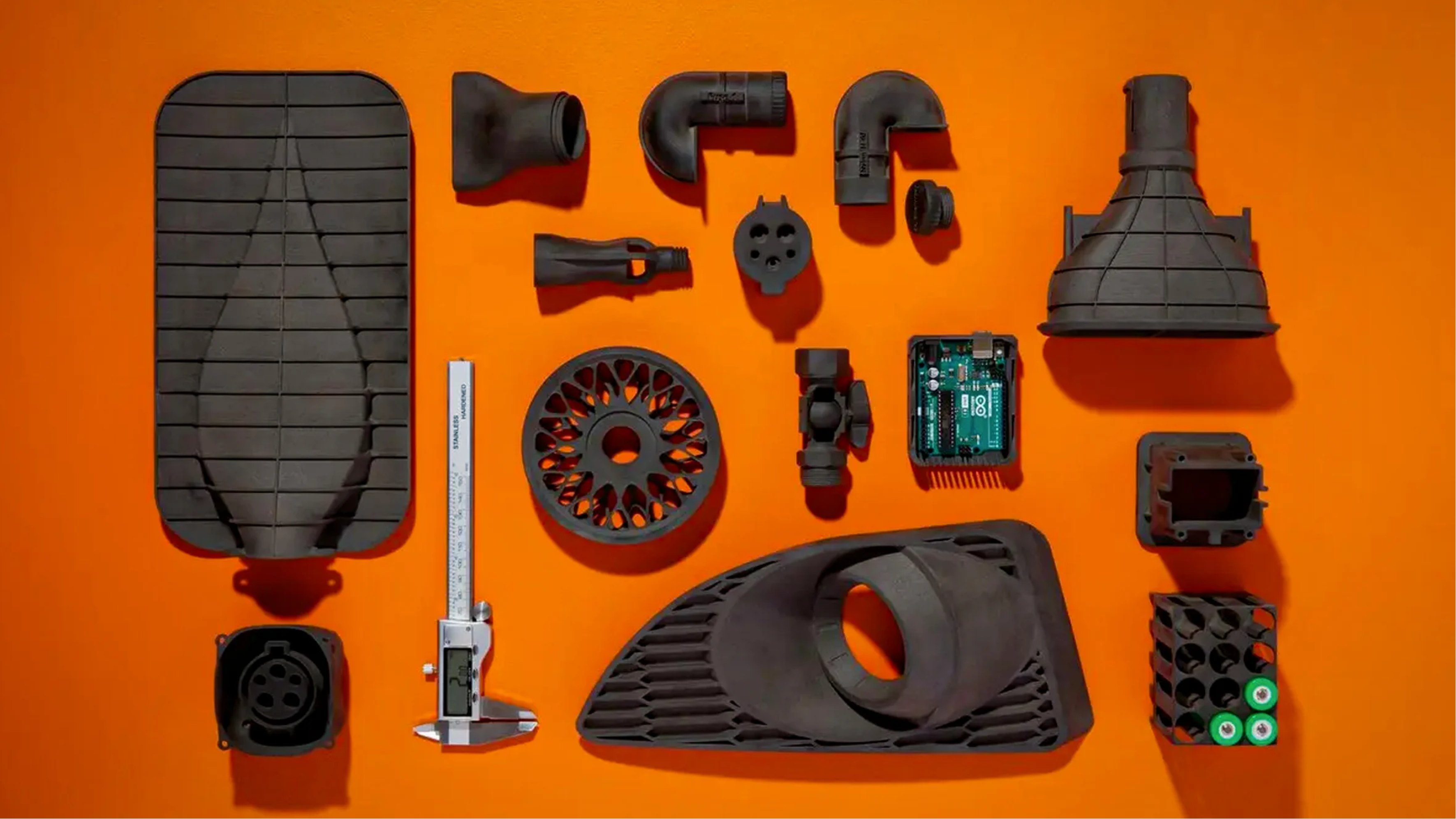
3D printing technologies can be used to create a wide range of products, from medical devices to consumer products. The technology is used to create prototypes and finished products, as well as to produce parts and components for larger products. 3D printing can also be used to create customized products, such as personalized jewelry or home décor.
3D printing technologies are also used to create molds and patterns for traditional manufacturing processes. For example, a 3D printed mold can be used to produce a large number of castings in a short amount of time. This process is often more cost-effective than traditional methods of manufacturing.
Advantage of 3D Printing Technology
The 3D printing industry has opened up a variety of business opportunities. For example, businesses can use 3D printing technologies to create customized products quickly and cost-effectively. Additionally, businesses can offer 3D printing services to create prototypes and molds for traditional manufacturing processes.
The 3D printing industry is also creating opportunities for individuals to start their own businesses. For example, individuals can use 3D printing technologies to create custom products, such as jewelry or home decoration. Additionally, individuals can offer 3D printing services to businesses, such as prototyping and mold-making.
3D Printing Technology – How it Works
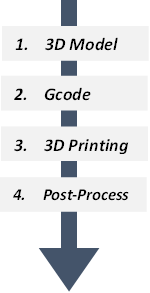
Any 3D printing process begins with a 3D digital model, which may be made using a number of 3D software programs, such as Computer-Aided Design (CAD) programs or by scanning a physical object using a 3D scanner. The design is then "sliced" into layers, making it into a file that can be read by the 3D printer, which called “Gcode” file. Gcodes instruct 3D printers on every action that printer must take in order to print the object, including movements, speed, temperatures, and much more.
The 3D-printed material is subsequently layered in accordance with the process and design. As previously said, there are several distinct types of 3D printing technologies, which use various methods to process various materials to produce the finished product. Industrial prototype and production applications today frequently incorporate functional plastics, metals, ceramics, and sand.
3D Printing Process
3D printers use diverse processes to handle different materials in various ways. There are several processes which to handle 3D printing, Deposition or Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) is the most common and readily identifiable technique, which extrudes polymers in filament form using a heated extruder. None of the 3D printing processes are presently accessible as plug-and-play options since there are several steps to perform both before pressing print and after the component has been taken out of the printer. Additionally, preparing and converting files may take a lot of time and effort, and many sections may require finishing process like support removal, polishing, coating, painting, or other types of conventional finishing touches.
In this article, we’ll focus on the Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) printing process, explaining its inner workings, material options, and much more.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
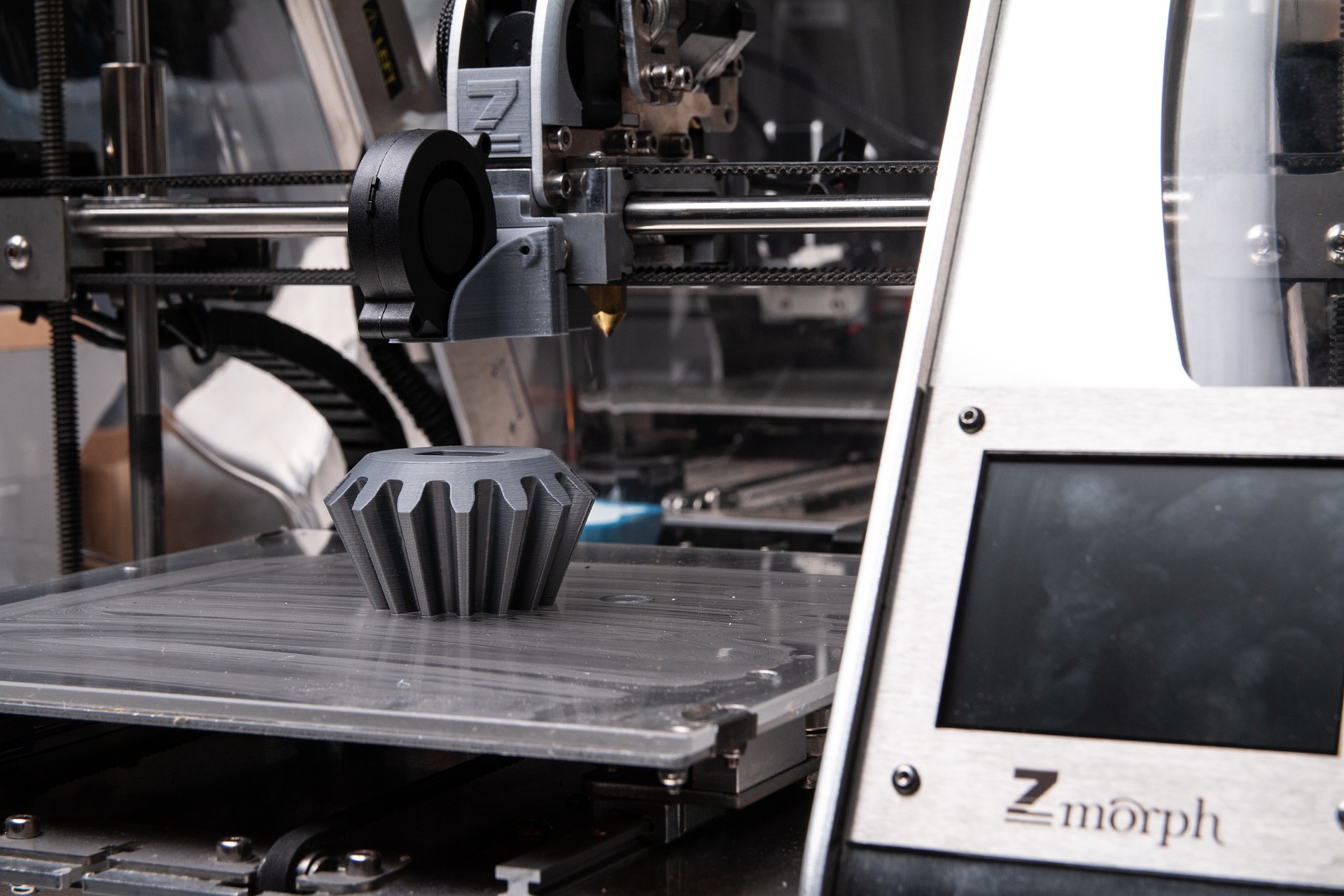
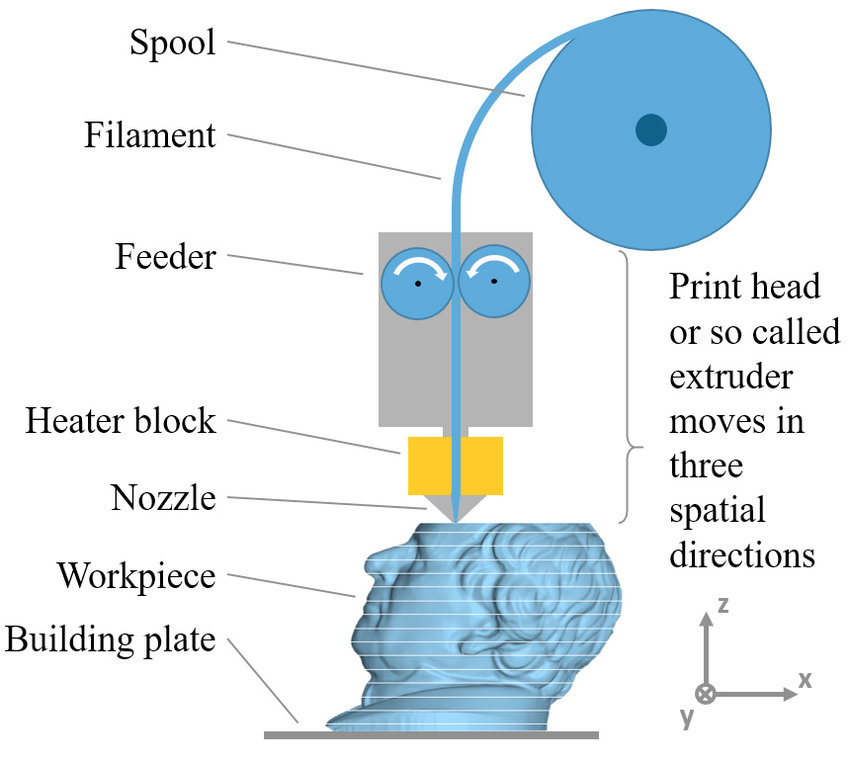
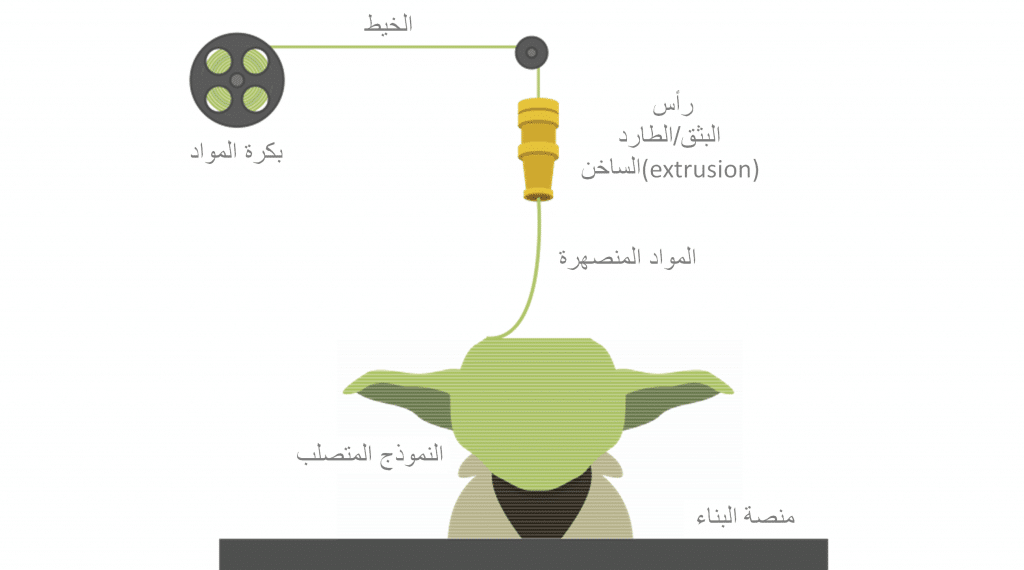
Fused deposition modeling, or FDM for short, is a type of 3D printing technology that uses a filament of thermoplastic material that is melted and extruded layer by layer to form an 3D object. In FDM, a computer-controlled extruder head melts the thermoplastic filament and deposits it in a controlled pattern to build up the object layer by layer. The extruder head is instructed by the Gcode file to ensure the correct shape and size of the object.
As a result, a typical FDM 3D printer pushes a polymer-based filament through a heated nozzle, melting the material and depositing it in 2D layers on the build platform. While the layers are still heated, they fuse together to form a three-dimensional object.
FDM printers sometimes take a great deal of tuning and adjustment to achieve the degree of durability and quality found in other printing processes. In contrast to other 3D printing technologies such as resin and SLS, FDM is strongly reliant on physical movement; therefore, many FDM printer components, in addition to calibration, require frequent maintenance and attention: belt tension, extruder cleaning, rail lubrication, and even part replacement, such as hot end nozzles. Also, poor filament dimensional accuracy can cause a variety of extrusion challenges, resulting in complex 3D printing.
FDM Materials and Their Applications
FDM Materials and Their Applications
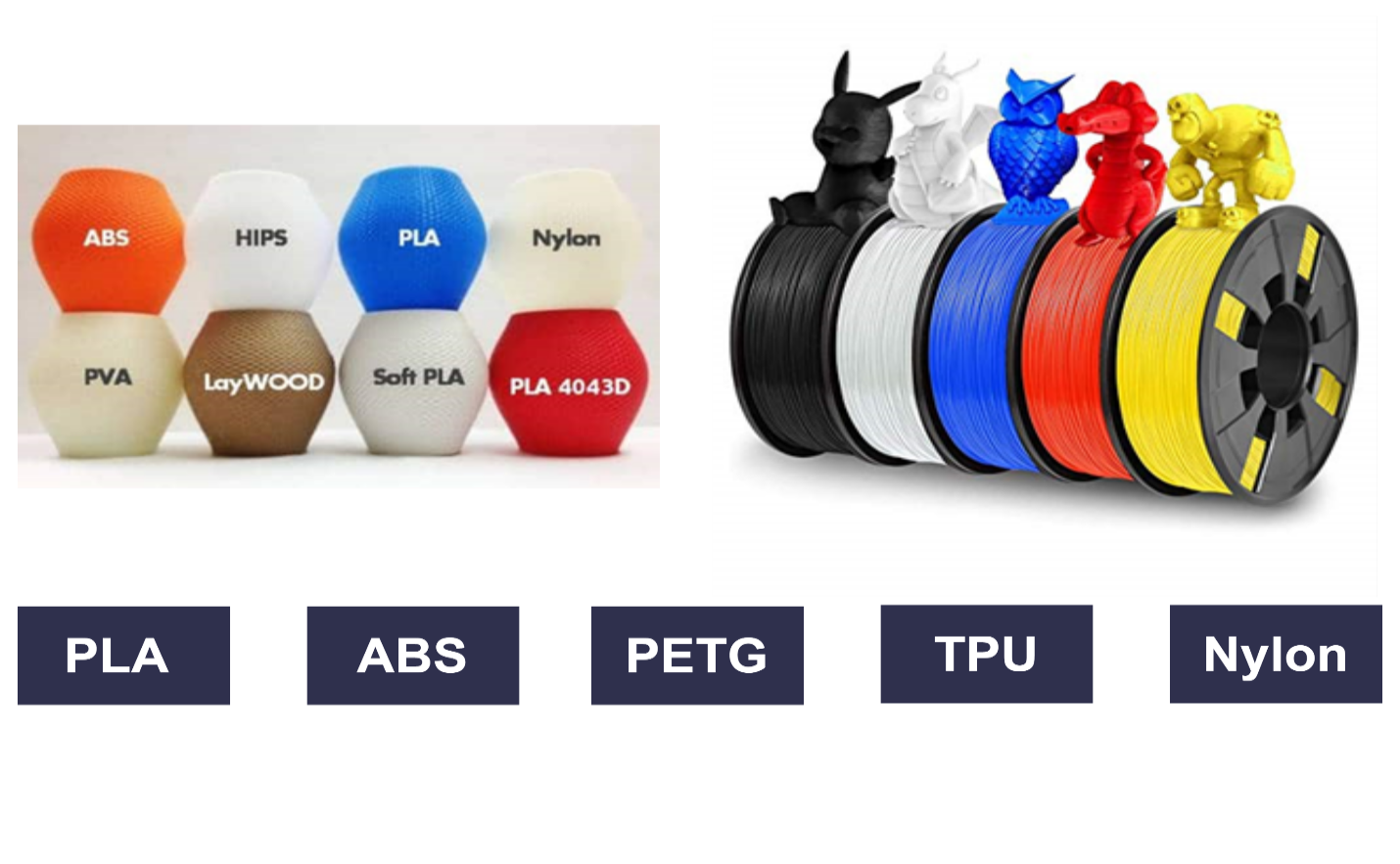
The materials for FDM 3D printing are all different kinds of thermoplastics and typically come in spools of filament that are fed into the 3D printer’s extrusion system.
The most popular FDM materials include PLA, a natural polymer made with starchy crops such as corn and sugarcane, and which is very easy to 3D print with; ABS, a strong and durable plastic used by industry in general, notable for producing Lego bricks; and PETG, a PET variant plastic known for its durability and heat resistance.
Other less popular FDM filaments include traditional plastics such as nylon, TPU and other specialty and exotic materials such as those with carbon fibers, wood, and even metals.
PLA (Polylactic Acid)
PLA is a biodegradable and environmentally friendly filament material that is commonly used in consumer and hobbyist 3D printing. It is known for its smooth, glossy finish, and is a popular choice for creating models, prototypes, and toys.
PLA is the most popular material used in FDM 3D printing. It’s safe, affordable, easy to print, and has outstanding material properties. You can use PLA filament for a wide range of applications, and it comes in an equally diverse range of composites and colors.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)
ABS melts and cools without altering its chemical properties. That makes it an interesting 3D printer filament, even more considering the relatively low temperatures required for melting.
ABS was the most popular material for 3D printing until PLA arrived on the scene. Still, it remains one of the best material choices for printing affordable, durable parts, being especially relevant in commercial applications such as rapid prototyping.
In addition, ABS provides excellent quality finishes when handled properly. It’s also suitable for use in relatively high-temperature applications, for example creating 3D printer parts.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-modified)
PTEG has taken the main stage for 3D printing materials in recent years. As an easy-to-print, food-safe, durable, and affordable material, it’s largely displaced ABS as the second most popular filament — next to PLA.
Because of its high strength, impact resistance, and temperature resistance compared to PLA, PETG is often used for practical applications that need to accommodate regular use and a bit of flexibility.
TPU (Flexible)
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), as the name indicates, are essentially polymers with rubber-like properties that make them exceedingly flexible and durable. As a result, TPE is widely utilized in the manufacture of automobile parts, home appliances, and medical supplies.
Nylon
Nylon is a tough, flexible, and lightweight material that is often used to create objects with complex geometries, such as gears and mechanical parts.
Nylon, also known as Polyamide (PA), is a popular family of synthetic polymers used in many industrial applications. As a filament for 3D printing, it excels where strength, flexibility, and durability are key requirements.
Each filament material has its own advantages and disadvantages, and the best choice will depend on the specific requirements of the project. Some of the factors that should be considered when choosing a filament material include the required strength and durability, the desired aesthetic qualities, and the intended end-use of the object.
Choosing the right 3D printing material is a crucial aspect of the 3D printing process as it affects the strength, durability, and overall quality of the final product.
The future of 3D printing materials is exciting, with new materials and advancements in technology constantly emerging. From biodegradable and eco-friendly materials to materials that mimic the properties of metals and ceramics, the possibilities for 3D printing materials are seemingly endless.
Sketchat - 3D Printing Services
Sketchat - 3D Printing Services
3D printing services. These services can be used to produce customized products, as well as to produce components for larger products. The services are often cost-effective, as they require minimal setup and can be completed quickly.
With Sketchat, the leading platform of 3D printing services and 3D model gallery, offers the following exciting services for its customers:
Prototype Design and Development: We help bring your ideas to life by creating 3D prototypes that can be used for testing.
Rapid Prototyping: Our state-of-the-art 3D printing technology allows us to produce prototypes in a fraction of the time so you can get your prototype in your hands as soon as possible.
Custom 3D Printing: Whether you need a custom-fit part for your latest invention or a unique gift for a friend, our team of experts can help. We offer a wide range of materials, colors, and finishes to choose from, so you can create a one-of-a-kind item that`s just right for you.
Material Selection Assistance: Our knowledgeable team will work with you to determine the best material for your needs, taking into account factors like strength, flexibility, durability, and cost.
3D Model Gallery: Our 3D model gallery is a great place to start. Browse our collection of thousands of models created by talented artists from around the world, or upload your own designs to share with the community.
Online Printing Services: Our online printing service makes it easy to order your 3D-printed parts and prototypes anywhere, anytime. Simply upload your design, select your materials and options, and place your order. Our team will handle the rest!
Conclusion
Conclusion
3D printing technologies have revolutionized the way products are designed and manufactured. They have opened up new opportunities for innovation and excellence were opened in various fields, from medical devices to aviation and space industries, unique and specialized consumer products. 3D printing technologies can be used to unlock the future. So why not start exploring the possibilities of 3D printing today?!