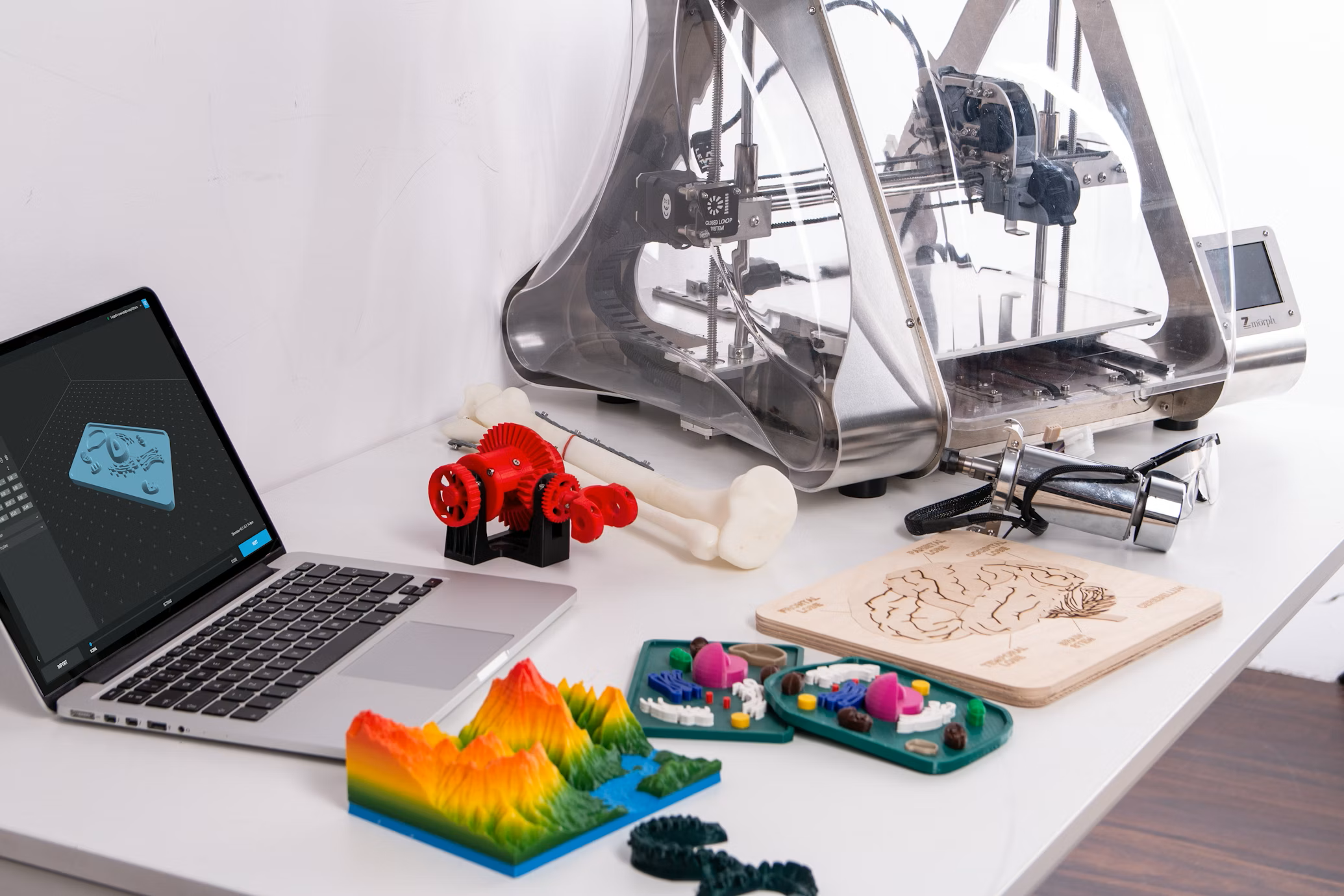
In today's rapidly advancing technological landscape, innovations continually reshape our world, compelling us to adapt and embrace new tools that transform digital concepts into tangible realities. Among these advancements, the ability to convert 2D images into 3D models has emerged as a remarkable development, particularly captivating for photography enthusiasts and designers alike. This process not only breathes new life into photographs but also enables the creation of personalized and intricate designs.
Understanding the Process
At its core, converting a 2D image into a 3D model involves interpreting the depth and structure inherent in a flat image. This transformation can be achieved through various methods, utilizing both online and offline tools tailored for different expertise levels.
How Does It Work?
One prominent technique is photogrammetry, which reconstructs a 3D model by analyzing multiple photographs taken from different angles. Specialized software processes these images, triangulating points to create a comprehensive three-dimensional representation. This method has been widely used in fields such as archaeology, architecture, and gaming to produce accurate 3D models of real-world objects.
Steps Involved in Photogrammetry
● Image Capture: Photograph the object from various angles to capture its complete geometry.
● Overlap: Ensure significant overlap between consecutive images for precise point matching during processing.
● Lighting: Use even lighting to minimize shadows and reflections that could interfere with the reconstruction process.
Image Processing
● Importing: Load the captured high-quality images into photogrammetry software such as Meshroom, Agisoft Metashape, or RealityCapture.
● Alignment: The software identifies common features across images and aligns them to reconstruct camera positions.
● Point Cloud Generation: A dense point cloud is created, representing the spatial coordinates of the object's surface.
● Mesh Creation: The point cloud is converted into a mesh, forming the object's surface geometry.
● Texturing: Textures from the original images are applied to the mesh to produce a realistic appearance.
While this process may seem straightforward, challenges can arise. For instance, creating a 3D-printable model of a handmade sculpture requires capturing a series of photographs from different angles. After processing them through photogrammetry software, a detailed 3D model suitable for 3D printing can be generated. However, potential obstacles may emerge, and it's advisable to begin such projects under professional guidance or outsource the work to experts, saving time and resources.
Popular Photogrammetry Software
● Meshroom: An open-source photogrammetry software that generates 3D models from photographs.
● Agisoft Metashape: A professional photogrammetry tool known for its high accuracy and extensive capabilities.
● RealityCapture: A fast and user-friendly software recommended for both beginners and professionals, capable of creating high-quality 3D models.
By adhering to fundamental photogrammetry principles, one can create accurate and detailed 3D models from 2D photographs, facilitating various applications in digital modeling and 3D printing.
Real-Life Application
Consider a scenario where a company aims to transform its logo into a 3D-printed keychain. The aforementioned steps — from image preparation and vectorization to 3D modeling — serve as an effective pathway to convert the logo into a 3D-printable model.
Advancements in AI: NeuralLift-360
For those interested in converting 2D images into tangible 3D models, recent advancements in artificial intelligence have further expanded the possibilities. One such technology is NeuralLift-360, a framework designed to transform 2D photographs into 3D objects with full 360° views. This AI-driven approach utilizes depth-aware neural radiance representation (NeRF) and is guided by denoising diffusion models.
By introducing a ranking loss, NeuralLift-360 can operate with rough depth estimations in various scenarios. Additionally, it employs a CLIP-guided sampling strategy to ensure coherent guidance. This method significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art baselines in generating plausible 3D objects from single images.
The ability to convert images into 3D models opens up a myriad of possibilities for 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals. By selecting the appropriate method and tools, one can effectively bring 2D designs to life, creating customized and functional 3D-printed objects. As technology continues to evolve, these processes are likely to become even more streamlined and accessible, further expanding the horizons of 3D modeling and printing.